SUBNETTING CALCULATION
In this section, you are expecting to show the calculation on how to identify the IP address that was assigned for the Online Learning System Server based on the information given in the project scenario. Explain the concept and show the calculation to identify the IP address.
For the following scenario, a class A IP addressing scheme 60.0.0.0/12
has been proposed and 4 subnets have been identified.
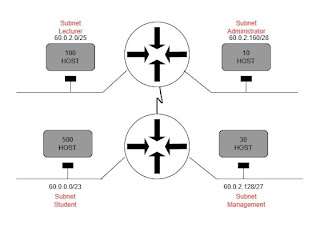
The first subnet which holds a total number of 500 hosts are made for the students followed by 100 hosts in the second subnet for the lecturers followed by 30 hosts in the third subnet for the management and 10 hosts in the fourth subnet for the administrators.
Subnet 1 – Student: 500 hosts
Subnet 2 – Lecturer: 100 hosts
Subnet 3 – Management: 30 hosts
Largest subnet = 500 host
Quantity of host = 2H – 2 ≈ 500
2H = 29 (more than 500)
When H = 9, 29 – 2 = 512 – 2 = 510 > 500
This is the situation: 60 . 0 . 0000 000X . XXXX XXXX
Next,
Subnet 0: 60 . 0 . 0000 000X . XXXXXXXX
Subnet 1: 60 . 0 . 0000 001X . XXXXXXXX
Subnet 2: 60 . 0 . 0000 010X . XXXXXXXX
Subnet 3: 60 . 0 . 0000 011X . XXXXXXXX
.
.
.
Subnet Broadcast: 60 . 0 . 1111 111X . XXXXXXXX
So, the IP for 1st subnet:
For 500 host,
60.0.0000 000X . XXXX XXXX
Then, from subnet 0:
Network Address: 60 . 0 . 0000 0000 . 0000 0000
IP Range: 60 . 0 . 0000 0000 . 0000 0001 – 60 . 0 . 0000 0001 . 1111 1110
Broadcast Address: 60 . 0 . 0000 0001 . 1111 1111
So, the IP for 2nd subnet:
For 100 host,
Take subnet 1 from previous subnetting: 60 . 0 . 0000 001X . XXXX XXXX
Quantity for the host:
2H – 2 ≈ 100
So, 2H = 27 (more than 100)
H = 7, 27 – 2 = 126 > 100
So, this is the situation: 60 . 0 . 0000 001X . XXXX XXXX
Subnet 0: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 0XXX XXXX
Subnet 1: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1XXX XXXX
Subnet 2: 60 . 0 . 0000 0011 . 0XXX XXXX
Subnet Broadcast: 60 . 0 . 0000 0011 . 1XXX XXXX
Then, from subnet 0:
Network Address: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 0000 0000
IP Range: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 0000 0001 – 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 0111 1110
Broadcast Address: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 0111 1111
For the IP for 3rd subnet:
For 30 host,
Take subnet 1 from previous subnetting: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1XXXXXXX
Quantity of host:
2H – 2 ≈ 30
So, 2H = 25 (more than 30)
H = 5, 25 – 2 = 30 >= 30
So, this is the situation: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1XXX XXXX
Subnet 0: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 100X XXXX
Subnet 1: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 101X XXXX
Subnet 2: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 110X XXXX
.
.
.
Subnet Broadcast: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 111X XXXX
Then, from subnet 0:
Network Address: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1000 0000
IP Range: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1000 0001 - 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1001 1110
Broadcast Address: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1001 1111
For the IP for 4th subnet:
For 10 host:
Take subnet 1 from previous subnetting: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 101X XXXX
Quantity of host:
2H – 2 ≈ 10
So, 2H = 24 (equal or more than 10)
H = 4, 24 – 2 = 14 > 10
So, this is the situation: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 101X XXXX
Subnet 0: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1010 XXXX
Subnet Broadcast: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1011 XXXX
Then, from subnet 0:
Network Address: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1010 0000
IP Range: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1010 0001 - 60 . 10 . 0000 0010 . 1010 1110
Broadcast Address: 60 . 0 . 0000 0010 . 1010 1111
Decimal form of Network Address for subnet 0: 60.0.2.160/28